Why Is the Co-Extruded Wood Plastic Great Wall Board Redefining Modern Architectural Surfaces?
Understanding the Material
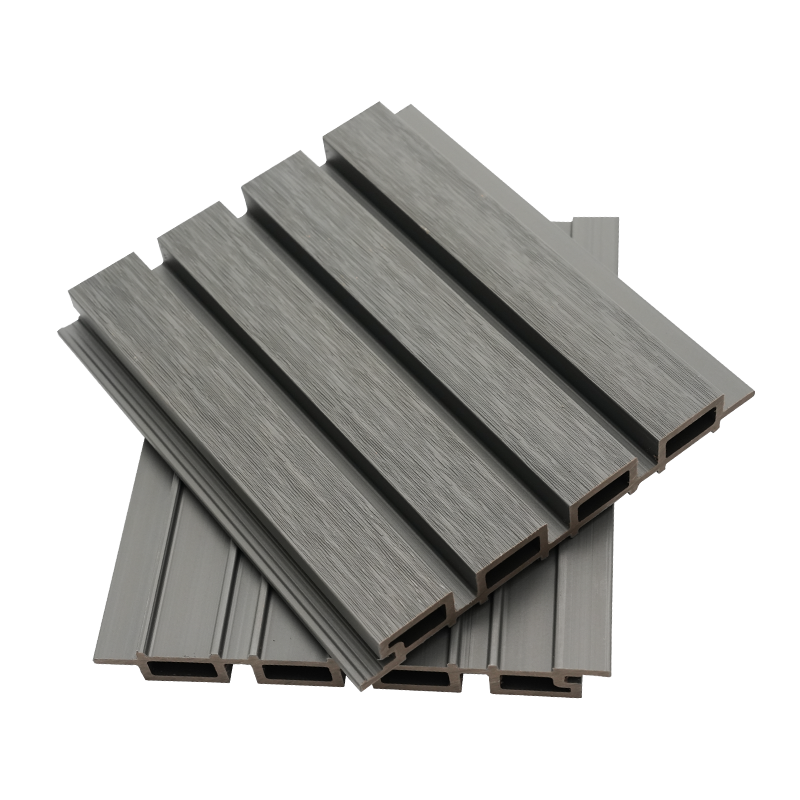
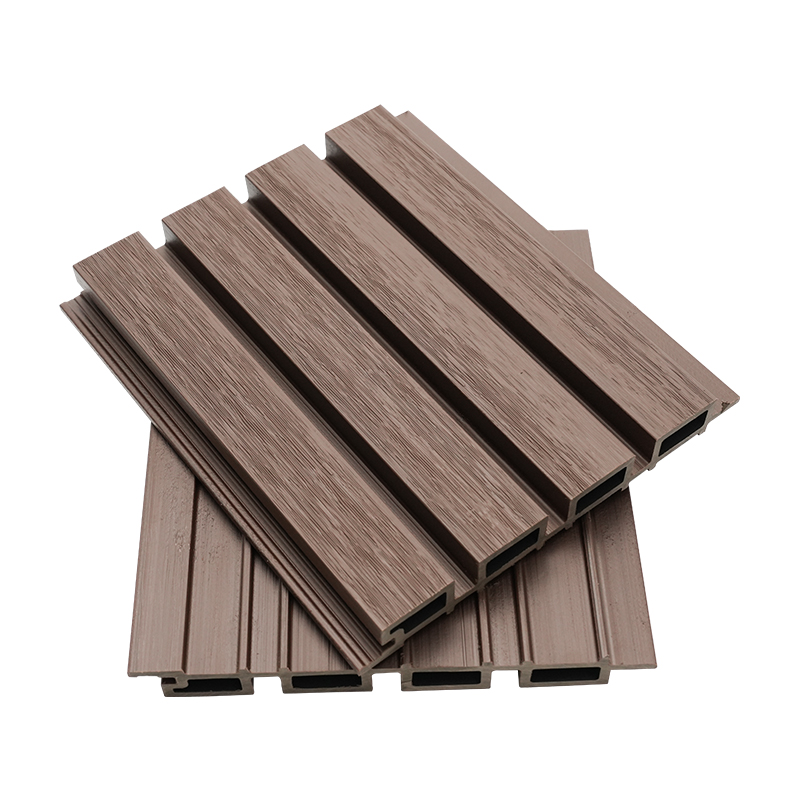
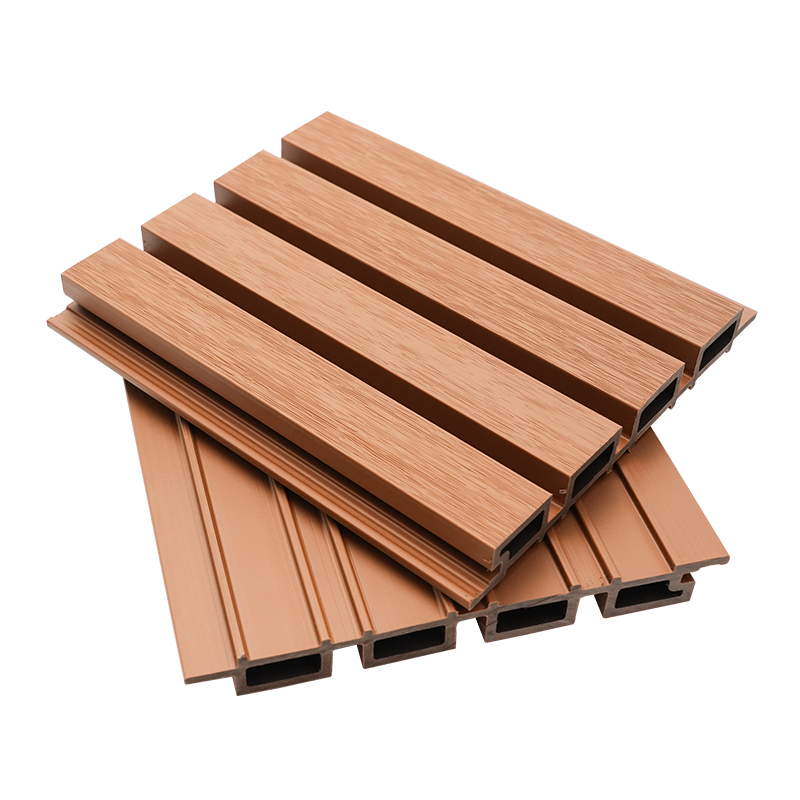
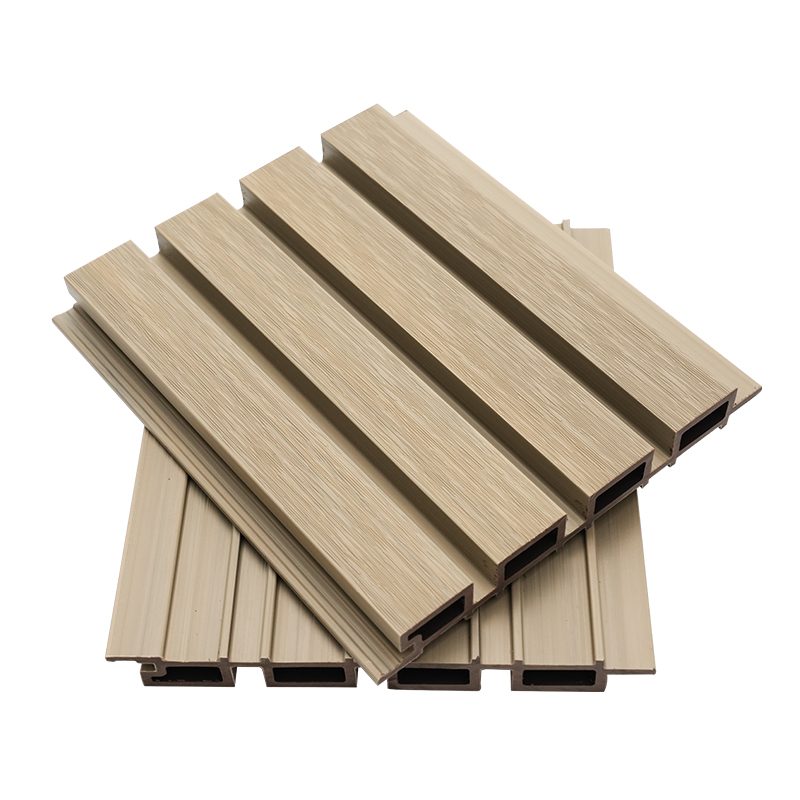
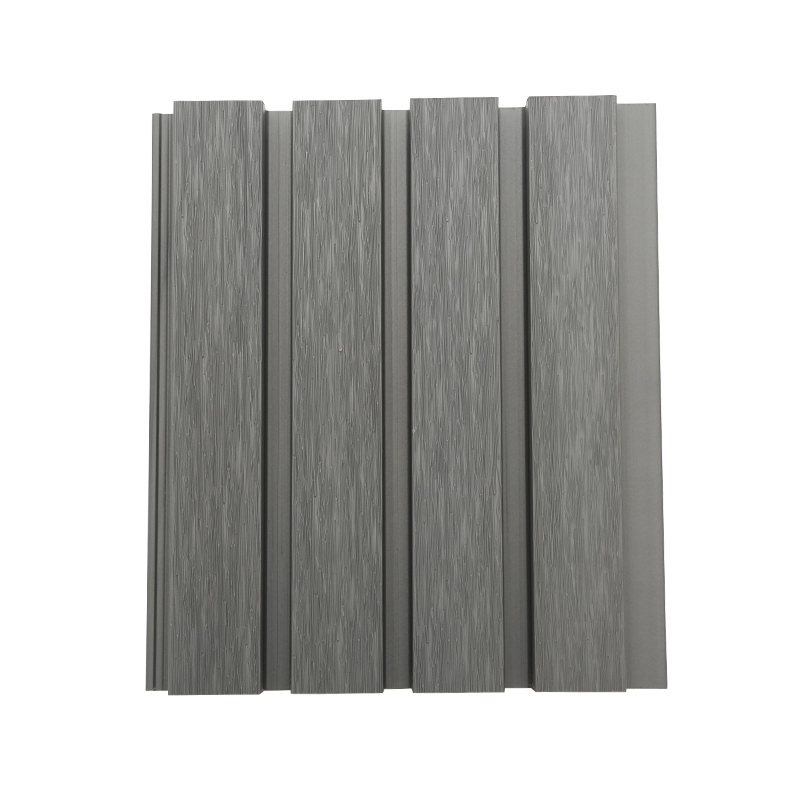
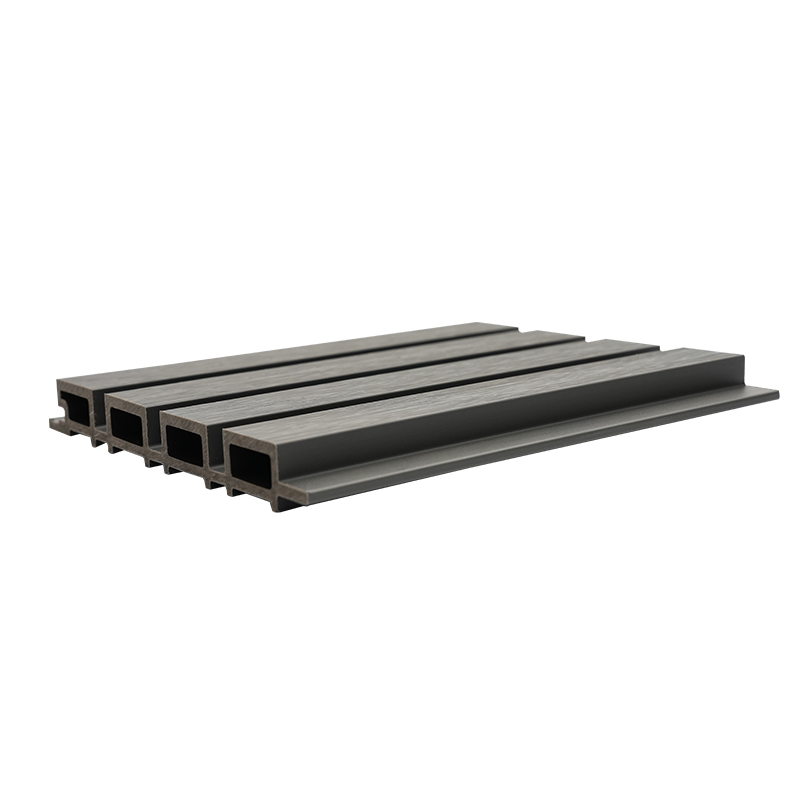
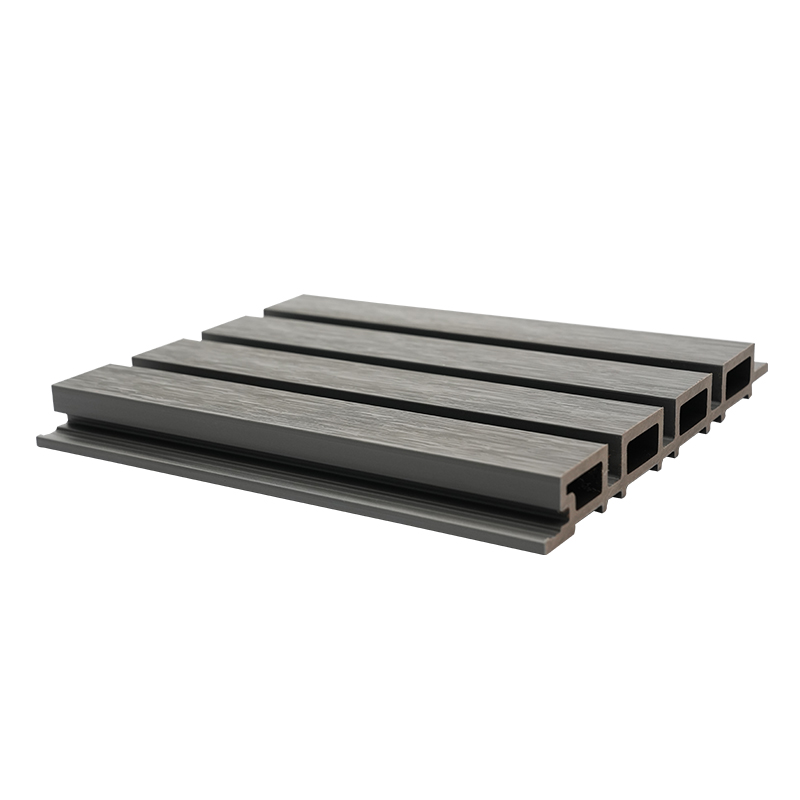
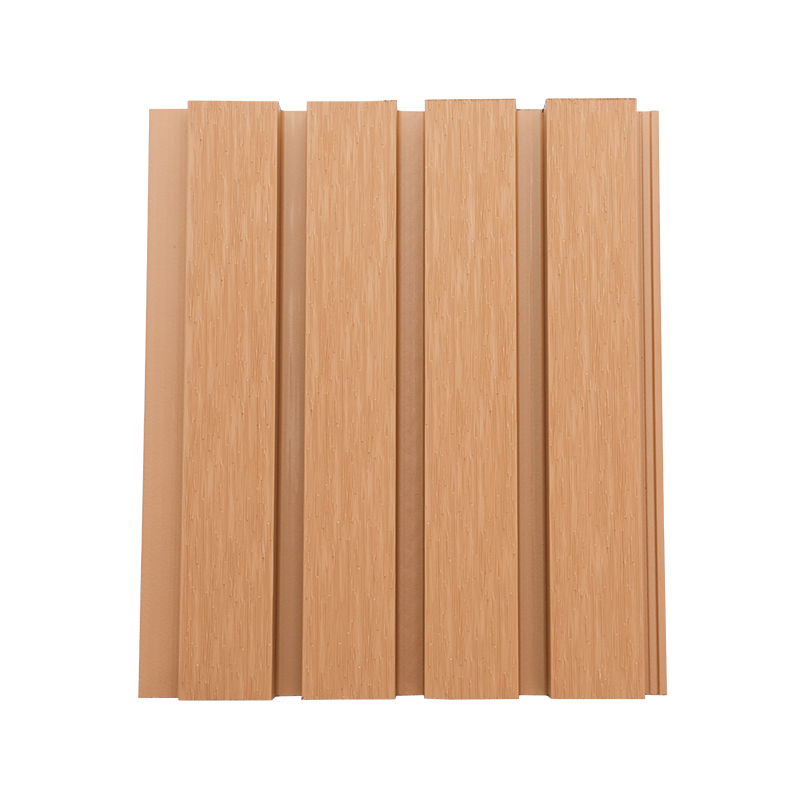
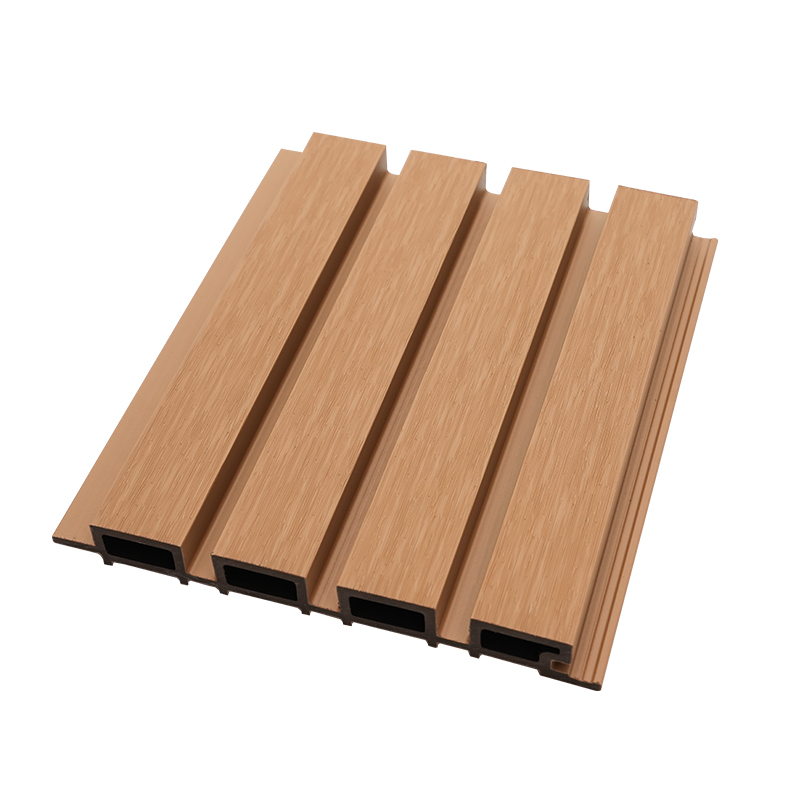
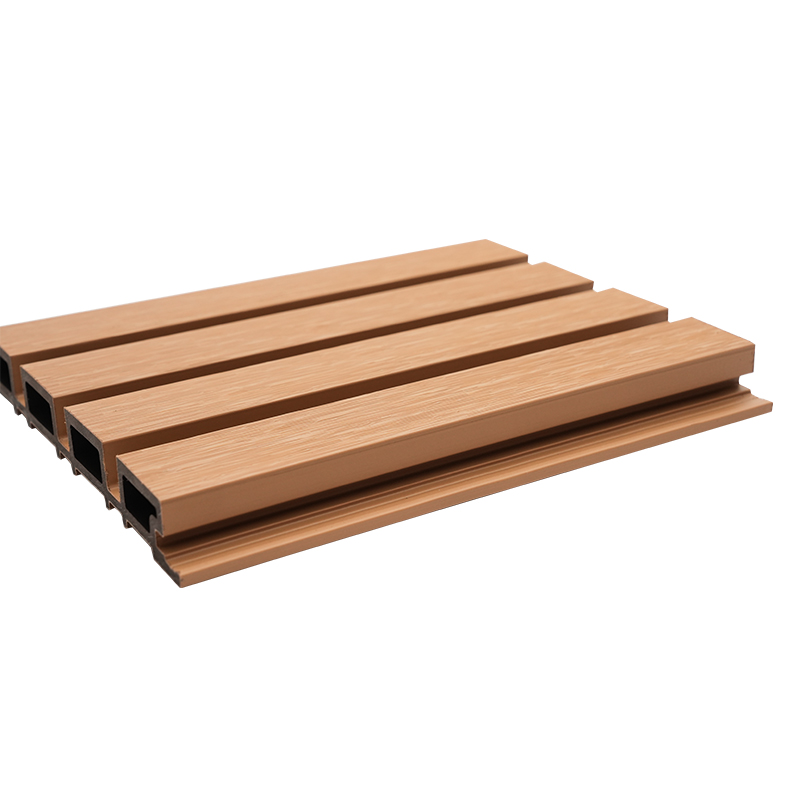
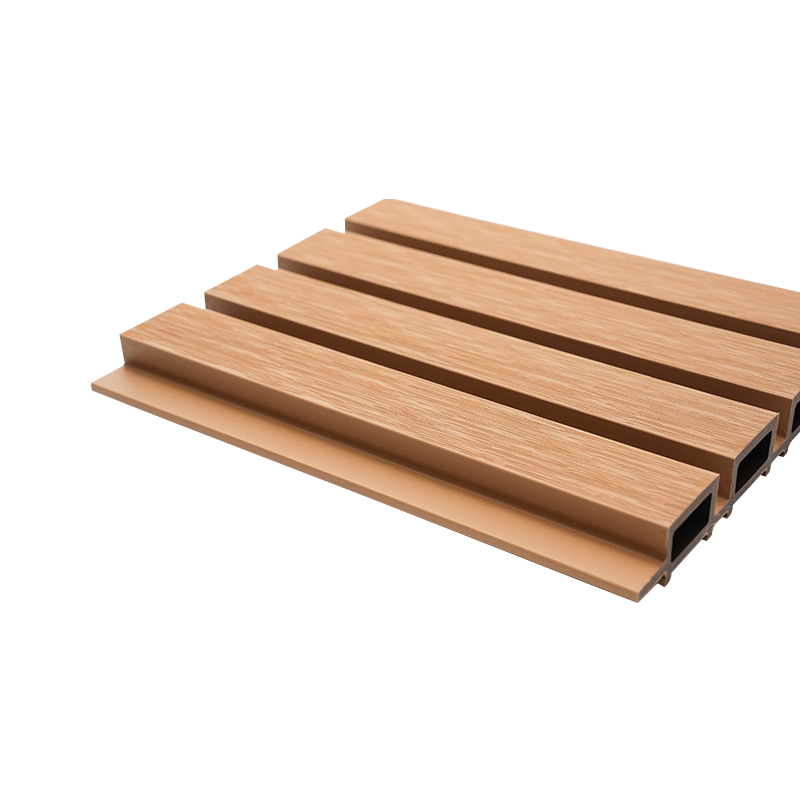
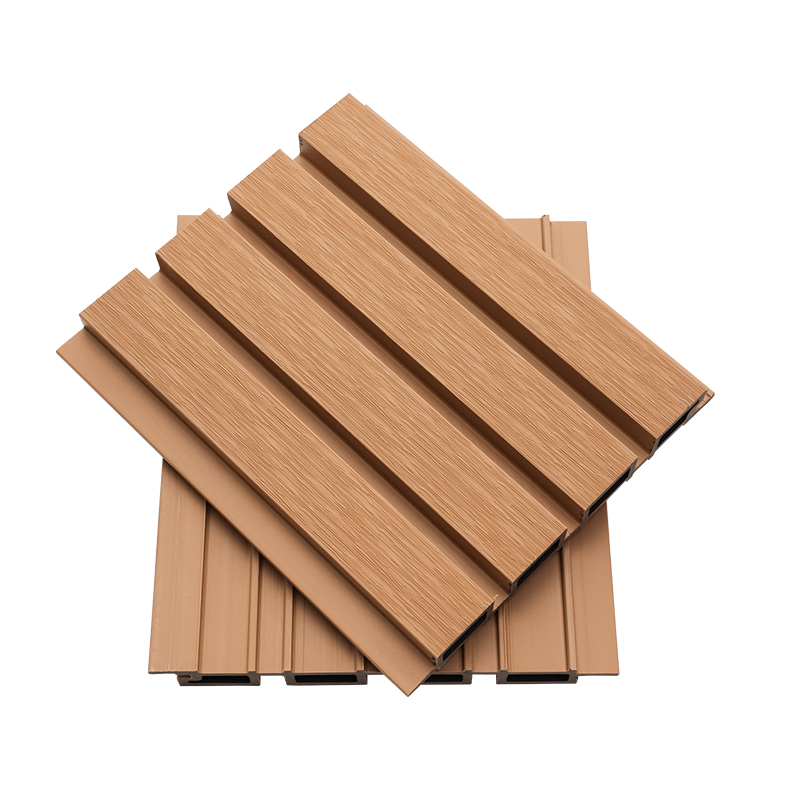
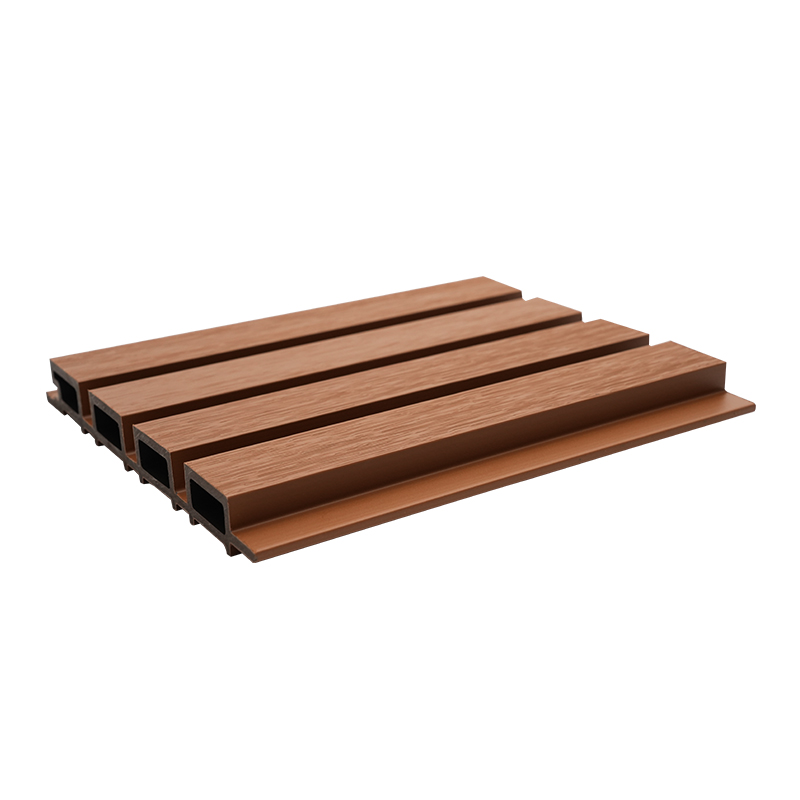
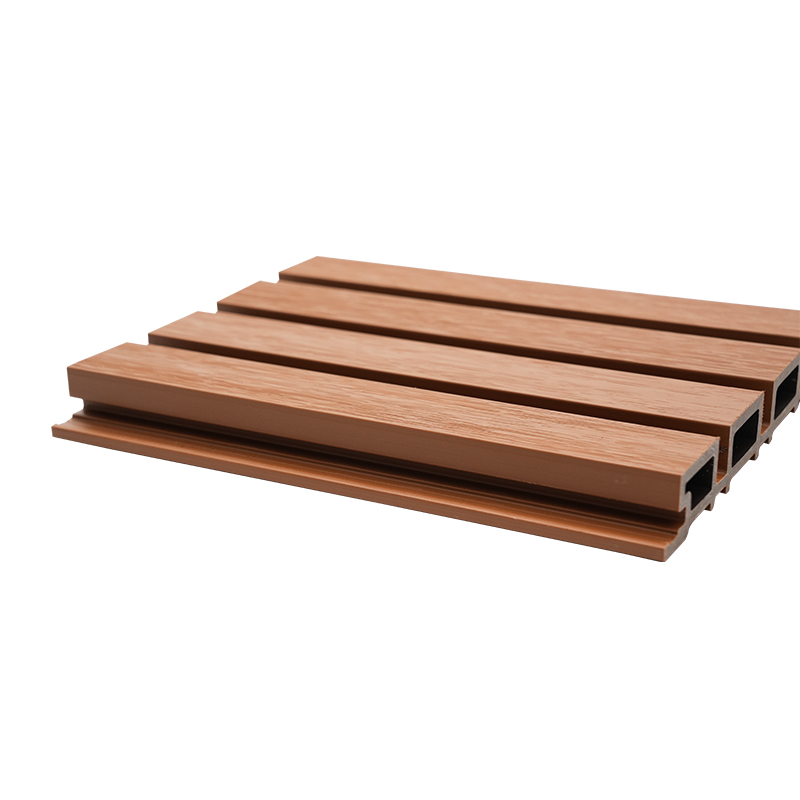
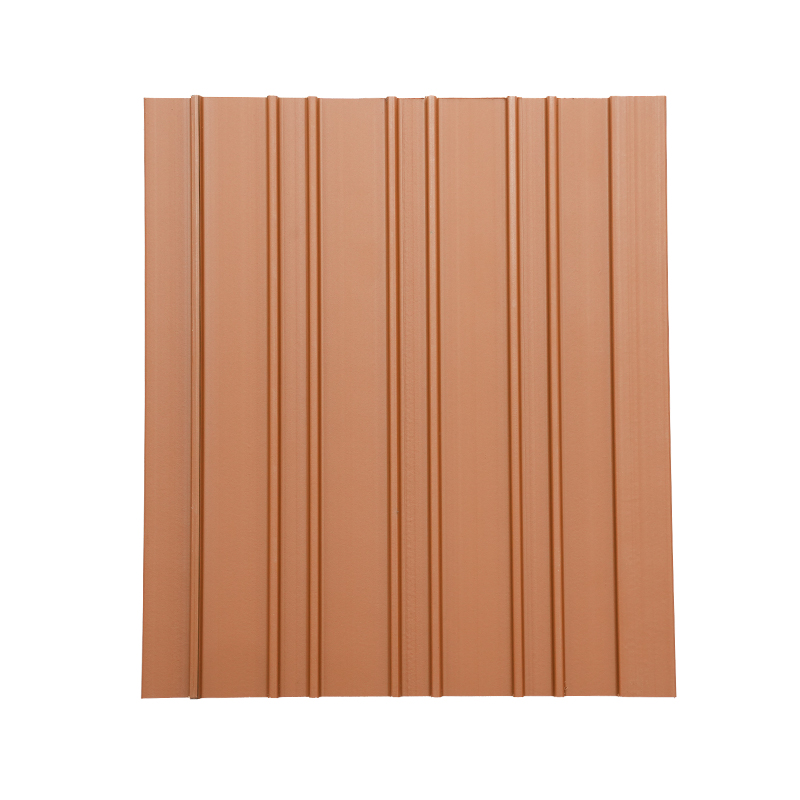
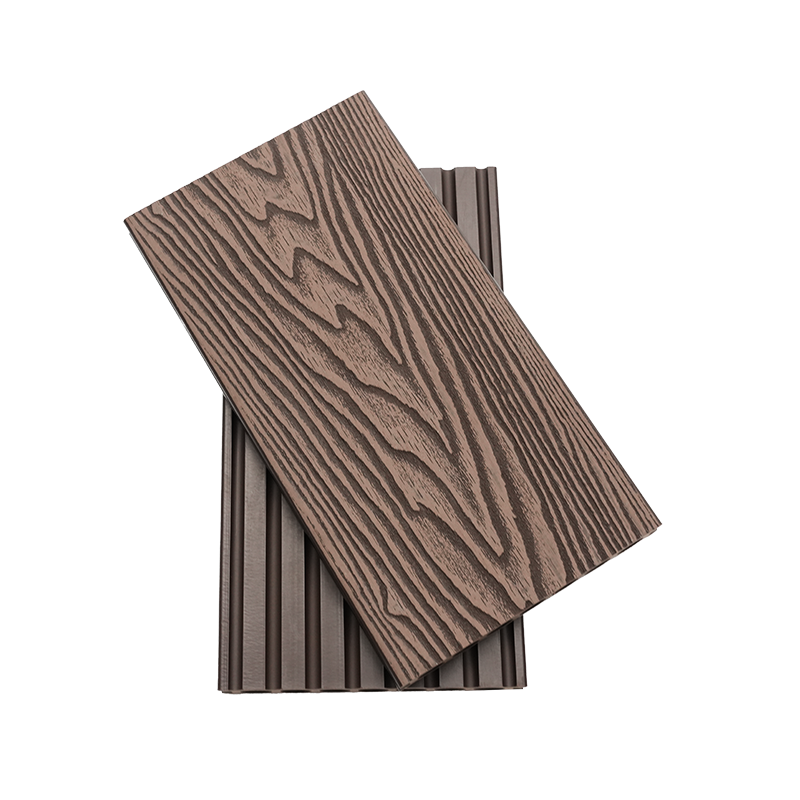
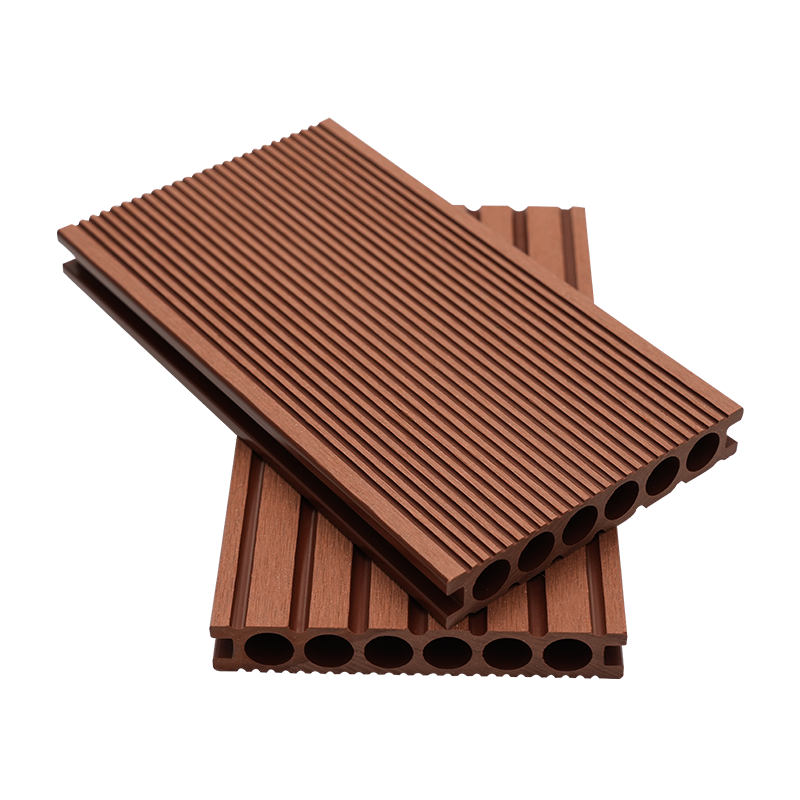
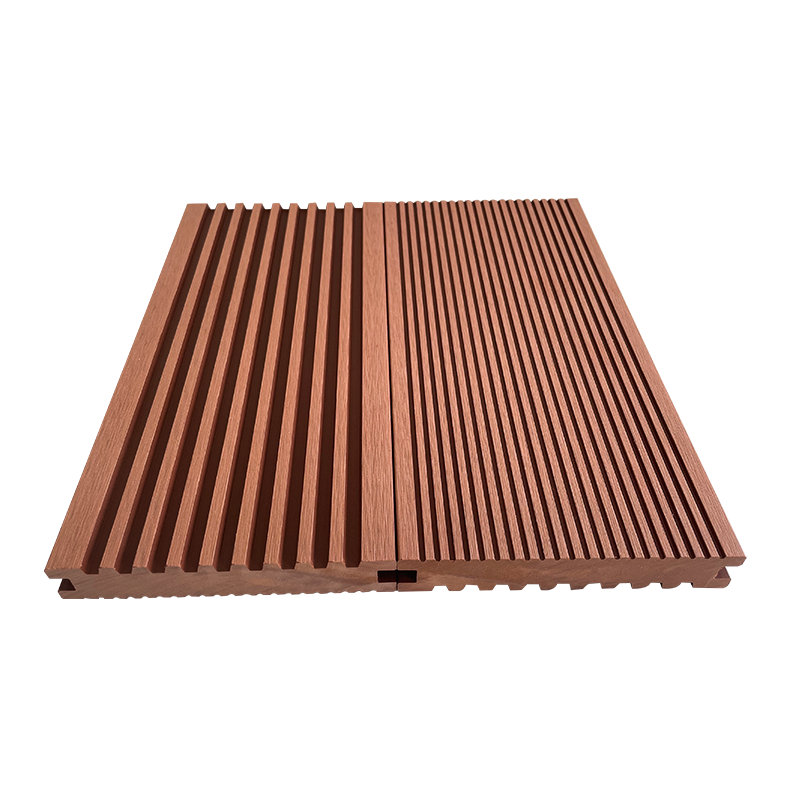
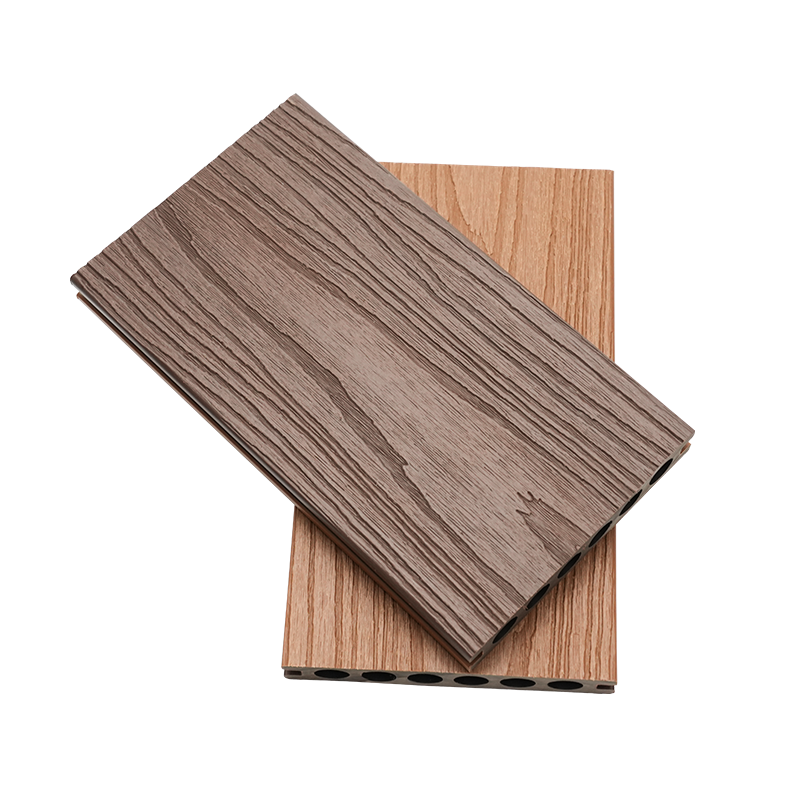
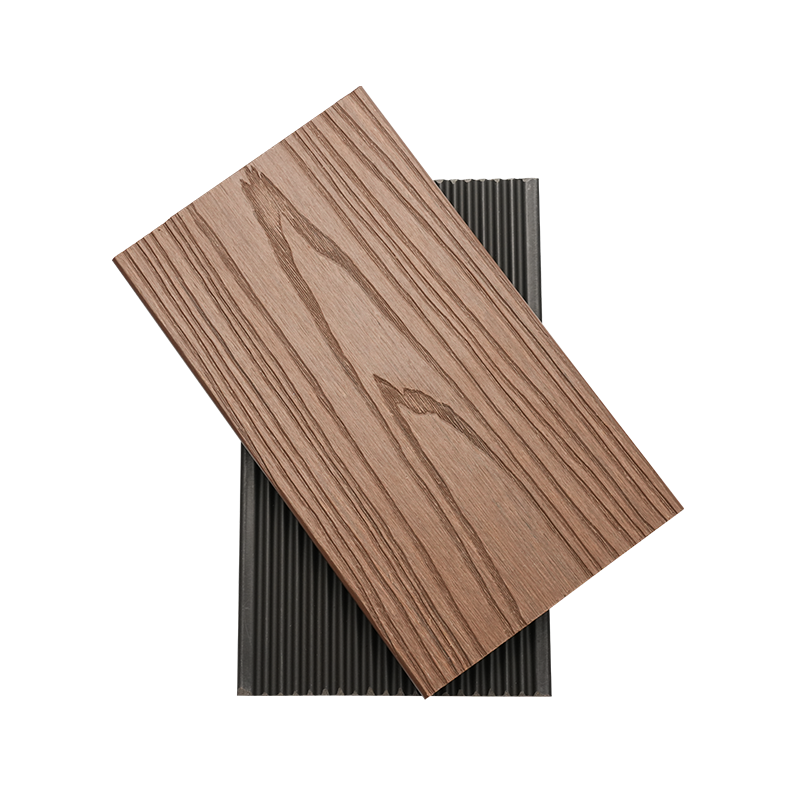
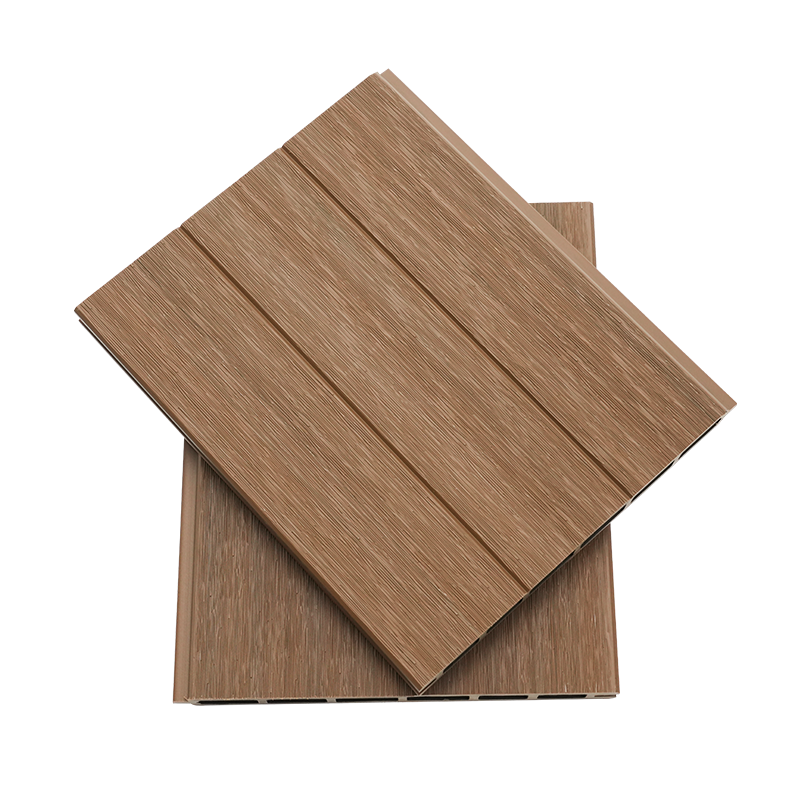
A Co-Extruded Wood Plastic Great Wall Board is a next-generation architectural surface that blends advanced co-extrusion methods with wood-plastic composite technology. The name “Great Wall Board” comes from its distinctive grooved profile, which resembles the layered appearance of traditional wall cladding.
Unlike single-material panels, this system uses a dual-layer structure: a protective polymer cap fused with a composite wood-plastic core. The result is a product that delivers both the natural charm of wood and the durability of engineered polymers, positioning it as a game-changer in modern construction and design.
The Science of Co-Extrusion
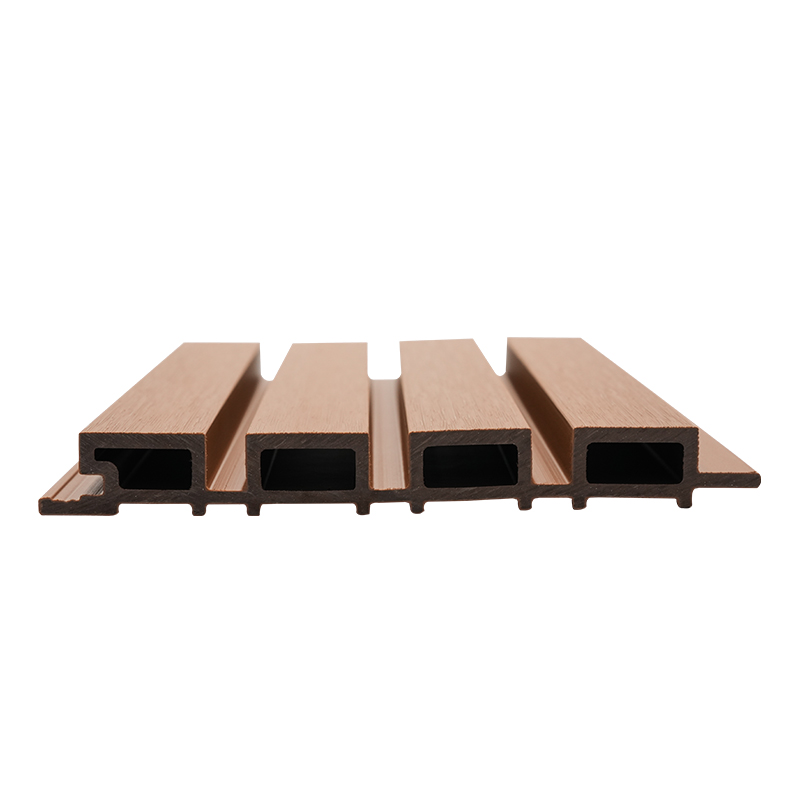
The co-extrusion process integrates multiple layers of materials during a single production cycle.
- Core Layer: A dense blend of wood fibers and thermoplastic resins that provides structural strength and rigidity.
- Cap Layer: A high-performance polymer shell that enhances UV resistance, prevents stains, and minimizes surface scratches.
This layered architecture ensures superior performance compared to conventional wood composites, offering greater resistance to weather extremes, wear, and long-term fading.
Technical Advantages
Architects and builders are increasingly turning to this material for its proven performance benefits:
- Weather Resistance: Protective capping prevents sun damage and surface cracks.
- Moisture Protection: The core absorbs minimal water, avoiding rot or swelling.
- Dimensional Stability: Resists warping and expansion under temperature fluctuations.
- Safety Compliance: Many boards meet fire-resistance standards for modern construction.
- Low Maintenance: No need for painting or sealing—cleaning with water is often sufficient.
These features make it highly attractive for projects demanding both longevity and visual quality.
Applications in Architecture
The design flexibility of this cladding makes it suitable for a wide range of projects:
- Residential: Decorative façades, garden walls, ceilings, and interior panels.
- Commercial: Shopping centers, hotels, and corporate office exteriors.
- Public Infrastructure: Transit stations, schools, and municipal facilities that require durability with minimal upkeep.
- Interior Design: Acoustic wall treatments and feature walls that combine beauty with function.
Its adaptability bridges the gap between structural necessity and aesthetic creativity.
Environmental Contributions
One of the strongest arguments for adopting this product is sustainability.
- Recycled Content: Typically made from reclaimed wood fibers and plastics, reducing waste.
- Forest Conservation: Lowers reliance on virgin timber resources.
- Long Service Life: Extends beyond 20 years, minimizing replacement frequency.
- No Toxic Chemicals: Unlike treated wood, it avoids harmful preservatives or paints.
These attributes align with global green building standards, helping developers meet stricter environmental certifications.
Performance in Harsh Climates
Field applications demonstrate its resilience under varied conditions:
- Intense Sunlight: UV-resistant capping reduces fading.
- Heavy Rainfall: Waterproofing minimizes swelling or surface damage.
- Freezing Conditions: Maintains integrity against freeze-thaw cycles.
- Tropical Humidity: Prevents mold, mildew, and moisture buildup.
This climate versatility is a critical advantage for international adoption.
Design Flexibility
Architects value the ability to achieve both function and aesthetics. The material offers:
- Multiple shades and finishes that replicate natural wood.
- Deep grooves and profiles that enhance shadow and texture.
- Customizable dimensions for different structural needs.
- Compatibility with contemporary and traditional building styles.
Such design freedom allows for greater creativity while still ensuring long-term performance.
Market Growth Outlook
The global market for advanced cladding materials is expanding rapidly. Driving factors include:
- Urban growth and demand for durable façades.
- Rising consumer preference for eco-friendly products.
- Government incentives for sustainable construction.
- The need for low-maintenance materials in large-scale developments.
Industry forecasts suggest that adoption of this technology will accelerate, making it a mainstream choice within the next decade.
Research and Industry Innovation
Continuous development is refining the material further. Manufacturers are focusing on:
- Improved UV stabilizers for longer-lasting color.
- Fire-resistant additives for enhanced safety.
- Smarter recycling methods for higher sustainability.
- Advanced extrusion precision for more consistent finishes.
For instance, Jiangsu Xuanhui New Material Technology Co., Ltd. has played a role in developing improved co-extruded composites, emphasizing both environmental responsibility and engineering strength.
Conclusion
The Co-Extruded Wood Plastic Great Wall Board is more than a cladding option—it represents the intersection of material science, environmental sustainability, and modern design needs. With its superior durability, low maintenance, and versatile aesthetics, it is setting new benchmarks in architectural surfaces.
As construction industries continue moving toward greener and longer-lasting materials, this innovative wall system is poised to redefine how we think about façades, both today and in the decades ahead.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى